Home » SysAdmin » Dual-Core vs. Quad-Core CPU: What's the Difference?
The CPU (central processing unit) is a key component of the computer that performs all the calculations and instructions required for it to function properly. Modern CPUs usually consist of multiple cores, i.e., processing units, that perform multiple tasks simultaneously.
Many CPUs used in PCs and laptops are dual-core (containing two CPU cores) and quad-core (containing four CPU cores).
In this article, you will learn the differences between a dual-core and quad-core CPU.

A dual-core processor is a CPU that has two processing units in one integrated circuit. The cores work simultaneously to achieve a much faster operating speed than a single-core processor. The cores can handle the tasks simultaneously because each core has its own cache memory and controller.
With the increase in CPU speed, the amount of heat generated also increases exponentially. Dual-core CPUs were introduced mainly with the purpose of improving performance and reducing the amount of heat generated by distributing the workload across two units. Less heat is generated as dual-core systems use about the same amount of energy as single-core CPUs.
Below is an example of an AMD dual-core CPU:

The first dual-core CPU was released by Intel in 2004, codenamed Intel Pentium D. The CPU was a significant step forward in processor technology, paving the way for further improvements in multi-core processor technology.
A quad-core processor is a CPU that has four processing units in a single integrated circuit. The cores operate simultaneously in conjunction with other circuits, such as cache, memory management, and I/O ports.
Quad-core processors came in 2006 as a successor to dual-core processors. The first quad-core processor was released by Intel, named Core 2 Quad. The processors were a major milestone for multicore systems as they provided greater speeds and better multitasking and computing performance.
Overall, quad-core processors offer improved performance, better multitasking capabilities, and efficiency over single-core and dual-core processors. They are ideal for demanding tasks, such as video editing, 3D modeling, and gaming.
The image below is an example of an Intel quad-core CPU:

While the key difference between dual-core and quad-core processors is the number of cores, they also differ in other important factors. Other crucial features are clock speed, power consumption, app support, processor architecture, etc.
The following table sums up the key differences between a dual-core and quad-core processor:
| Category | Dual-Core Processor | Quad-Core Processor |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A CPU with two cores (processing units). | A CPU with four cores (processing units). |
| Performance | Handles basic tasks, capable of handling some tasks simultaneously, but with a decreased performance. | Handle more complex tasks and runs multiple programs simultaneously without a decrease in performance. |
| Speed | Faster than a single-core processor, but usually slower compared to a quad-core processor. | Faster overall than single-core and dual-core processors, especially when running multiple programs simultaneously. |
| Power Consumption | Consumes less power than a quad-core processor. Thus, it provides better battery life for portable devices. | Usually consumes more power than a dual-core processor, shortening the battery life of portable devices. However, advances in technology are now significantly reducing the power consumption of each core, activating the cores only when they are required. |
| Heat | A dual-core processor generates less heat than quad-core processors. | Quad-core processors generate more heat than dual-core processors because they use more energy to power each core. |
| Price | Less expensive compared to quad-core processors. | More expensive than dual-core processors. |
| Use Cases | Suitable for non-demanding, basic tasks, like web browsing, word processing, and email exchange. | Suitable for more demanding tasks, such as video editing, gaming, running virtual machines, etc. |
| Future | Dual-core processors are currently used mostly in low-end machines, and they could become obsolete soon. Additionally, programs are becoming more complex and require more processing power, making dual-core CPUs a poor choice. | Quad-core processors have a longer lifespan than dual-core since programs and apps are more optimized for running on multiple cores. |
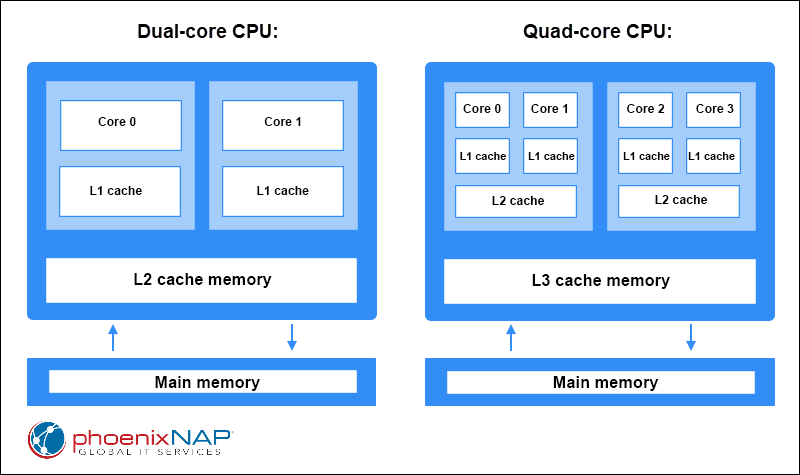
The following diagram shows the difference between an example architecture of a dual-core CPU and a quad-core CPU:
Determining if dual-core or quad-core processors are better depends on their purpose and what they will be used for. Each CPU caters to a different use case.
In general, quad-core processors offer better performance and multitasking capabilities because they have twice as many processing units as dual-core processors. More cores means they can handle more tasks simultaneously and execute instructions faster.
Note: If you are using Linux, see how to check CPU utilization using the command line.
Additionally, quad-core processors usually have higher clock speeds and larger cache sizes than dual-core processors, but this depends on individual CPU type. Cache memory is high-speed memory integrated into the CPU and used to temporarily store frequently accessed data and instructions needed by the CPU.
If you need a performant processor that supports demanding tasks, such as video editing or 3D modeling, quad-core is a better choice. Such tasks utilize the additional processing power of each core.
On the other hand, basic tasks, such as web browsing and word processing, don't require as much processing power, and a dual-core processor is sufficient.
Note: The actual performance of a processor varies based on its physical properties, such as clock speed, cache size, architecture, and manufacturing process, but also the software's support for multiple cores. Thus, when comparing processors, consider all the factors, and not just the number of cores.
This section covers the most frequently asked questions related to processors and offers advice on choosing the right kind of processor for your needs.
The number of processor cores you need depends on the use case and the purpose of the computer. If you plan to use specific software, research the system requirements for that software to get a better idea about what processor would be best for your needs.
Always pay attention to the processor's clock speed and cache size. These factors significantly impact performance, in addition to the number of cores.
Depending on the use case, the following general guidelines apply:
The tasks and processes that require more CPU cores are the ones that require a CPU to handle multiple threads of execution at the same time. More cores means that the task is accomplished efficiently because the work is divided among the available cores.
Some examples of tasks that benefit from more available CPU cores include:
Note: Some tasks are not optimized to take advantage of multiple processor cores, and a faster processor with fewer cores can sometimes be better than a slower processor with more cores. Always check the requirements of the software you plan to use before choosing a processor.
The difference in dual-core and quad-core CPU speed depends on multiple factors, including the clock speed, cache size, and the software that you are using.
A quad-core processor should provide a significant performance boost over a dual-core processor. The boost is especially helpful in multitasking scenarios and when using software optimized for multiple cores. However, not all apps are optimized for utilizing multiple cores. That means there may not be a significant performance improvement compared to a dual-core processor in such cases.
Quad-core CPUs can divide the workload across four cores, where each core handles a separate task. Task distribution improves system responsiveness. It also reduces the chance of the system slowing down or freezing.
A quad-core CPU is only faster than a dual-core CPU when a program can split its tasks across all the available cores, which is not the case with all software.
Scaling to cores is a software's ability to assign the right tasks to appropriate cores so that each core is processing information at its optimal speed. However, software usually splits its tasks sequentially or randomly across cores, which means that they don't reach their full potential.
For example, a demanding task can get assigned to a single core instead of being split across two or more. On the other hand, simple tasks can get assigned to other cores, which complete them much faster, and then wait idly for the hardest task to be completed.
In such cases, a dual-core processor with a higher clock speed would finish the task faster than a quad-core CPU with a lower clock speed.
The CPU architecture is also an important factor, as well as the amount of cache memory. For example, a newer dual-core CPU with a higher clock speed and more cache can outperform an older quad-core CPU that has a lower clock speed per core and less cache memory.
This article has compared dual-core and quad-core CPUs and explained the key differences between the two processor types. Choose quad-core CPUs if you need more computing power, and dual-core CPUs when you want to perform basic tasks.
Learn more about CPUs in our tutorial about the difference between a CPU and a GPU.